Implantology
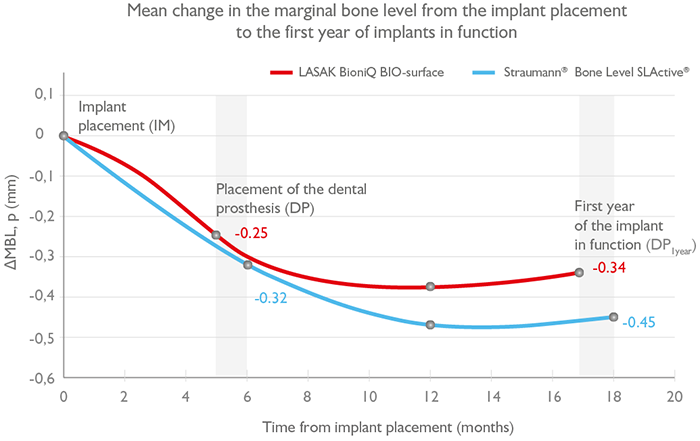
A high level of marginal bone conservation
The main factor affecting patient satisfaction following implant installation is the provision of good functionality and an optimal esthetic outcome. Natural-looking esthetics ensure the stability of the alveolar bone in accordance with the physiological dimension of soft tissue (biological width). This can be achieved only if the implant, framework and dental prosthesis work in perfect harmony. The results of the study/studies show that BioniQ products have this symbiosis. Thanks to this, the LASAK BioniQ ranks among the best brands in the field. Sources.
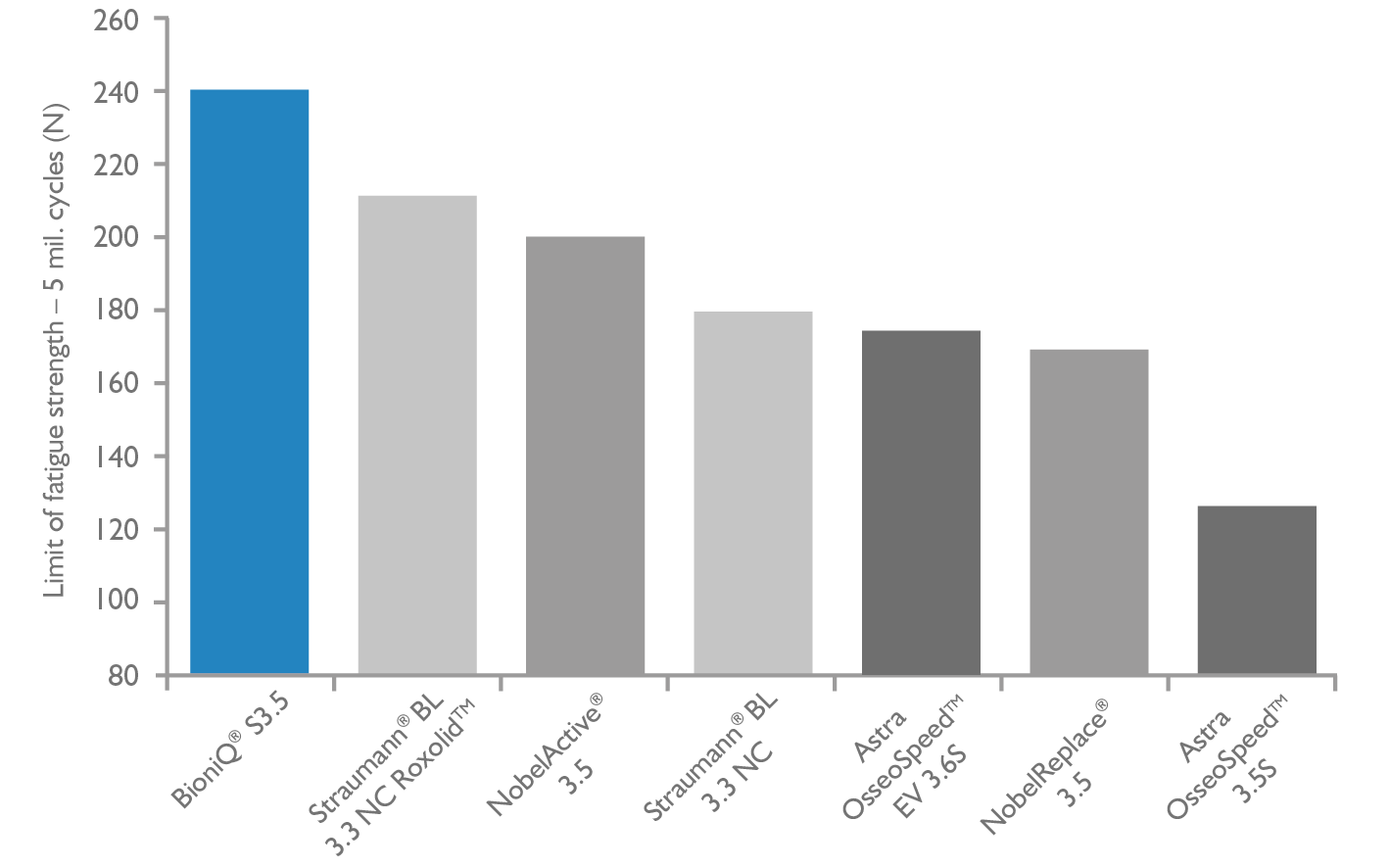
High fatigue strength of the implant-abutment connection (ISO 14801)
The stress of the implant and the abutment is examined through the use of a chewing kinematics strength test. The test consists of 5 million cycles, where the strength of the connection implant-abutment-screw is checked. This number of cycles corresponds to about 20 years of implant lifetime. Source
BioniQ clinical casebook
- The LASAK BioniQ implant system, highlighted in this clinical casebook, prioritizes both simplicity and effectiveness. It meets the rigorous demands for long-term functionality and esthetics in dental implantology. This contemporary system provides versatile instrumentation, accommodating both freehand and guided surgical techniques.Here you can download BioniQ clinical casebook
Case reports
- Total Tooth Reconstruction Using Dental Implants; doc. MUDr. Martin Starosta, Ph.D.: CSK Scientific PressTreatment with dental implants in patients with edentulous jaws faces many problems. First and foremost is the patient’s overall health and ability to undergo a relatively extensive surgical procedure. Another issue is the local sufficiency of the alveolar bone to place a sufficient number of implants. This involves planning the number and placement of implants. This consideration is directly related to the type of prosthetic reconstruction and the suitability of its use, not only with respect to the patient profile but also the properties of the materials used for prosthetic reconstruction.
- Finding the right dental implant prosthetics for long‐term success; Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc. M.Sc.: Implantologie Journal 3/2021Elderly patients usually want to enjoy their food without discomfort while being treated minimally invasively. They often have only a limited budget for their treatment, too. Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc., M.Sc. is well aware of this. He is, however, able to fulfil his patients’ high expectations by using our BioniQ implants, together with PORESORB-TCP bone graft.
- Implants and prosthetics for the ageing patient; Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc. M.Sc.: Implantologie Journal 9/2021
What questions does the implant dentist have to deal with from ageing patients and how can our narrow BioniQ Plus implants with the machined collar help?
- Guided surgery in case of low bone volume; Dr. Pavel Hyspler: Implantologie Journal 10/2021
If you want to implant in places with insufficient bone for classic implantation, there are several possibilities. BioniQ Guided Surgery seems to be one of them. Modern technologies bring the patient more comfort and, thus, greater satisfaction.
- Possible use of computer-assisted surgical procedures; Dr. Jiri Hrkal: Implantologie Journal 10/2022
Based on his many years of experience with guided surgery and dynamic navigation Dr. Jiri Hrkal reports, how current technologies, materials, procedures and LASAK BioniQ implants help him to treat his patients functionally, aesthetic and long-term stable and sustainable.
Clinical studies
- Retrospective study of a serie of pterygoid implants; Cea-Arestín P, Bilbao-Alonso A, Hernández-DeOliveira M.:Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2024. doi:10.4317/medoral.26633
- The influence of biological width violation on marginal bone resorption dynamics around two-stage dental implants with a moderately rough fixture neck: A prospective clinical and radiographic longitudinal study; Strnad J., Novák Z., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Dent & Ora Hea 2021; 7:6, 20-36.
- Marginal bone response of submerged and non-submerged osteoconductive alkali-etched implants in thick and thin biotypes: A 2-year clinical follow-up study; Novák Z., Strnad J., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(5):1184-1194.
- 5-Year Prospective Clinical Study of Early Loaded BioniQ Implants with Bioactive Alkali-Etched Surface. Results after 1-Year of Follow-up; Novák Z., Strnad J., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: LKS, 5/2018: 116–125.
- Influence of abutment height and implant depth position on interproximal peri‐implant bone in sites with thin mucosa: A 1‐year randomized clinical trial; Pico A., Martín-Lancharro P., Caneiro L., Nóvoa L., Batalla P., Blanco J.: Clin Oral Impl Res. 2019;00:1–8.
- Chronological Age as Factor Influencing the Dental Implant Osseointegration in the Jaw Bone; Papež J., Dostálová T., Chleborád K., Kříž P., Strnad J.: Prague Medical Report / Vol. 119 (2018) No. 1, p. 43–51
- Effect of abutment height on interproximal implant bone level in the early healing: A randomized clinical trial; Blanco J., Pico A., Caneiro L., Nóvoa L., Batalla P., Martín-Lancharro P. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2017;00:1–10.
- Development of Implant Stability During Early Healing of Immediately Loaded Implants; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Strnad J., Čapek L., Slezák R.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2012; 27 : 619–627.
- Changes in Stability After Healing of Immediately Loaded Dental Implants; Simunek A., Strnad J., Kopecka D., Brazda T., Pilathadka S., Chauhan R., Slezak R., Capek L.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, Vol. 25, No. 6, 2010, p. 1085–1092.
- Teeth in six hours; Šimůnek A., Vosáhlo T., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Sobotka M., Dufková D.: Implantologie Journal 8/2006.
- Early loading (4 weeks) of dental implants Impladent in maxilla and mandible – monitoring of the healing process using resonance frequency analysis; Štěpánek A., Strnad J., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz Vol. 14, No. 9, 2005.
- Reduced healing time of Impladent implants with bioactive surface; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J.: Quintessenz Vol. 13, No. 6, 2004.
- Internal sinus augmentation using porous resorbable calcium phosphate ceramic material; Nathanský Z., Strnad J., Veselý P.: Clin. Oral Impl. Res. Vol. 14, No. 4, 2003.
- Replacement of individual teeth with IMPLADENT implants – a 5 year report; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 7, No. 6, 1998.
- Extention of alveolar ridge without raising the mucoperiosteal flap using minimally-invasive dental implant surgery – a new step in effective implantology; Šmucler R., Barták P.: Implantologie Journal 2/2007.
- Reconstruction of cleft palate using implants – Case Report; Dostalová T., Holakovský J., Bartoňová M., Seydlová M., Smahel Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 16, No. 9, 2007.
- Is Lateral Sinus Lift an Effective and Safe Technique? Contemplations after the performance of one thousand surgeries; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Somanathan R. V.: Implantologie Journal 6/2007.
- Transversal Screw-retained prostheses fixed on dental implants; Podstata J., Kozisek E., Mulicek M.: Implantologie Journal 3/2007.
- Replacement of shortened dental arch using Impladent implants; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 4, No. 12, 1995.
- Screw-retained prostheses supported by implants; Nathanský Z., Šváb R., Rádlová Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 5, No. 12, 1996.
- A 5-year follow-up study on Impladent Dental Implants; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Krulichová I., Škrabková Z., Mounajjed R.: Quintessenz, Vol. 10, No. 10, 2001.
- Internal sinus floor elevation – new dental implantology possibilities; Nathanský Z.: Čes. Stomat. 103/51, 2003, 6:229-233.
- Stability time dependence of loaded and unloaded dental implants; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Kopecká D.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. Vol. 16, No. 4, 2005.
- STI-Bio titanium implants with bioactive surface design; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Novák J., Strnad Z., Kopecká D., Mounajjed R.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. 12, 2001.
- Long-term (9 years) experience with narrow diameter implants (2.9 mm); Podstata J., Hudler T., Novák J., Kožíšek E., Quintessenz, Vol. 2, No. 15, 2006.
- Effect of primary stability on early loaded implants; Štěpánek A., Strnad J., Strnad Z. Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. Vol 16, No. 4, 2005.
- Three-year multicentric study of osseointegrated Impladent implants; Šimůnek A., Štěpánek A., Zábrodský V., Nathanský Z., Strnad Z., Quintessenz, Vol. 6, No. 6, 1997.
- Alkali treatment – new concept of titanium implant surface modification; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J., Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
Clinical studies – abstracts
- Efecto de la altura del pilar en la pérdida ósea periimplantaria; Pico Blanco A.: Universidade de Santiago de Compostela 2021.
- Novák Z, Nesvadba R, Strnad J, Kamprle J, Strnad Z. Marginal bone level and biologic width dynamics in tissue-level and bone-level implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(S20):192. doi:10.1111/clr.134_13644
- Implants with an osteoconductive surface and a moderately rough neck – 3 years of follow-up; Nesvadba R., Novák Z., Strnad J., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(S19):303. doi:10.1111/clr.259_13509
- Stability assessment of immediately loaded alkali-etched implants; Nathanský Z., Strnad J., Strnad Z.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
- Alkali treatment – new concept of titanium implant surface modification; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
- Bioactive titanium implants for shorter healing period; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Štěpánek A.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 13, No. 4, 2002.
- Peri-implantitis, problems and solutions – a 2 year study; Novák Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 13., No. 6, 2004.
- Use of Impladent dental implants in edentulous jaws; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 5, No. 5, 1996.
- Three-year multicentric study of osseointegrated Impladent implants; Šimůnek A., Štěpánek A., Zábrodský V., Nathanský Z., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 6, No. 6, 1997.
- Using of dental implants in reconstructive surgery; Holakovský J., Mazánek J., Hubálková H., Nejedlý A., Tvrdek M.: To be published.
Experimental studies
- In Vitro Bioactivity Test of Real Dental Implants According to ISO 23317; Kolafová M., Šťovíček J., Strnad J., Zemek J., Dybal J.: JOMI, Vol. 32, No 6, 2017.
- Alkali–modified Titanium Surface Stimulating Formation of Bone–implant Interface; Strnad J., Macháček J., Strnad Z., Povýšil C., Strnadová M.: Key Engineering Materials, Vols 361-363, pp 749-752, 2008; Bioceramics 20, Nantes, France.
- Secondary Stability Assessment of Titanium Implants with an Alkali-Etched Surface: A Resonance Frequency Analysis Study in Beagle Dogs; Strnad J., Urban K., Povýšil C., Strnad Z., JOMI, Vol. 23, No. 3, 2008.
- Effect of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on the osteoconductivity of commercially pure titanium implants; Strnad Z., Strnad J., Povýšil C., Urban K.: International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, Vol. 15, No. 4, 2000, pp. 483–490.
- Early Interaction of Biomaterials with Dynamic Simulated Body Environment; Strnad J., Strnad Z., Protivínský J., Helebrant A.: in Proc. 5th Asian Symposium on Biomedical Materials (Yasuhiko Tabata ed.), Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, Hong Kong 2001, pp. 51–55.
- The effect of surface roughness and texture on bioactivity of titanium in vitro, in vivo; Strnad Z., Strnad J., Dalibová L.: Transactions of Sixth World Biomaterial Congress, USA, Vol. III, 2000, p. 1055.
- Effect of implant diameter and length on the stress caused in the surrounding bone by the occlusal forces; Himmlová L., Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Dostálová T.: Prakt. Zub. Lék., 48, 2000, pp. 155–163.
- The effect of bioactive surface on implant stability during healing; Strnad J., Urban K., Strnad Z.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 16, No. 4, 2005.
- Modelling of stress and deformation distribution around endosteal implants; Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 8, No. 12, 1999.
Experimental studies – abstracts
- Interaction of acid and alkali treated titanium with dynamic simulated body environment; Strnad J., Protivínský J., Mazur D., Veltruská K., Strnad Z., Helebrant A., Šesták J., J. Therm: Anal. Cal., Vol. 76, 2004, 17–31.
- Chemically treated titanium early surface activity detected in vitro; Strnad J., Protivínský J., Strnad Z., Veselý P.: Clin. Oral impl. Res. Vol. 13, 4, 2002.
- Modelling of stress and deformation distribution around endosteal implants; Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 8, No. 12, 1999.
- Bone-like apatite formation in titanium and silica glass; Strnad J., Helebrant A., Hamáčková J.: Glass Sci. Techn. – Glastechn.Ber. , Vol. 73, C1, 2000.
- Kinetics of bone-like apatite formation in simulated body fluid; Strnad J., Helebrant A.: in: Proc. 5th ESG Conference (eds. Helebrant A., Kasa S., Maryška M.), pp. B2 9–16, Czech Glass Soc., Praha, 1999.
Sources
LASAK, BioniQ BIO-surface: Novák Z., et al. 5-Year Prospective Clinical Study of Early Loaded BioniQ Implants with Bioactive Alkali-Etched Surface. Results after 1-Year of Follow-up.
Straumann®, Bone Level SLActive®: Hammerle CH., et al. Interim 1-year results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 2012; 23, 2012: 211–219. Sanz M., et al. Interim 3-year results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Impl. Dentistry and Related Res. 2015; 17, 2015, 234–246.